
In a nutshell: The article explores the similarities and difference between private and public clouds and will help you decide which is best for your organization.
The cloud has become a ubiquitous term in today’s tech landscape. Instead of relying on on-premises servers and hardware, cloud computing enables users to access shared computing resources over the internet, using a pay-as-you-go or subscription-based model. However, not all clouds are created equal. (Also, learn about different roles in the cloud.)
Businesses have a choice between private and public clouds, and each has its own unique set of benefits and challenges. While both have advantages and drawbacks, the right choice depends on your business needs, goals, and budget.
Private vs. Public Clouds: At a Glance
Before we discuss private vs. public clouds in detail, let’s look at their features at a glance.
| Private Cloud | Public Cloud |
| Dedicated and secure | Agile for innovation |
| Customizable | Reduced complexity |
| High scalability | Scalability, flexibility |
| Efficient | No maintenance costs |
| Expensive with high TCO | Potential for high TCO |
| Limited infrastructure | Minimal control |
| Minimal mobiles access | Flexible Pricing |
| Regulation compliant | Decreased security and availability |
What is a Public Cloud?
Public clouds are a widely used deployment model for cloud computing. Gartner states that “global end-user expenditure on public cloud services is expected to increase by 20.7% and reach $591.8 billion in 2023, compared to $490.3 billion in 2022”.
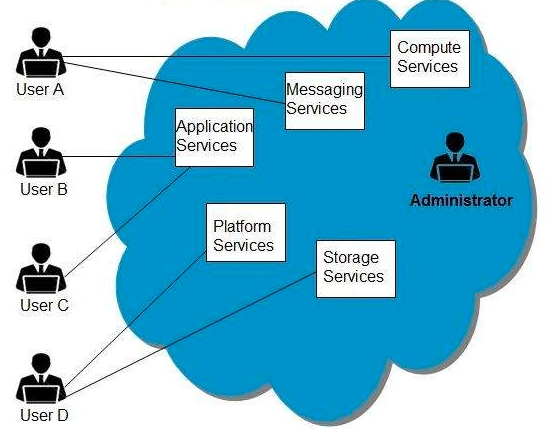

In a public cloud, a third-party service provider owns and operates cloud resources, such as servers and storage, and delivers them over the internet. The cloud provider handles all the hardware, software, and other necessary infrastructure, making it an attractive option for businesses and individuals. A well-known example of a public cloud is Microsoft Azure.
Advantages of Public Cloud
Let’s explore the advantages of using a public cloud.
- Less monetary burden: Public cloud providers often offer a pay-per-use model, which allows organizations to only pay for the computing resources they use, enabling them to avoid upfront costs associated with purchasing and maintaining their own infrastructure.
- Scalability: Public clouds are highly scalable and can quickly adjust to meet changing business demands. Organizations can easily scale up or down their computing resources to accommodate changes in workload or business needs.
- Flexibility: Public cloud providers offer a wide range of computing services and applications that can be easily accessed and deployed. This allows organizations to experiment with different tools and technologies without incurring additional costs.
- Zero maintenance: Since the cloud provider is responsible for the maintenance, patching, and updates of the hardware and software, organizations can focus on their core business operations, avoiding costs and time associated with maintaining their own infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
Here are a few disadvantages of a public cloud.
- Security and privacy: Public clouds are shared by multiple organizations, which can increase the risk of security breaches and data theft. While cloud providers typically have robust security measures in place, organizations are still responsible for securing their own applications and data in the cloud.
- Limited control: In a public cloud, organizations have limited control over their infrastructure and resources. This can make it challenging to customize the computing environment to meet specific business requirements.
- Cost uncertainty: While public clouds can be cost-effective for many organizations, pricing models can be complex and difficult to predict. Organizations may find that their costs increase unexpectedly as they scale their usage of cloud resources.
What is a Private Cloud?
A private cloud is a cloud computing environment dedicated to a single organization and is used exclusively by that organization’s employees, partners, or customers. IDC predicts “sending on private cloud services is expected to increase at a CAGR of 31% by 2025.”
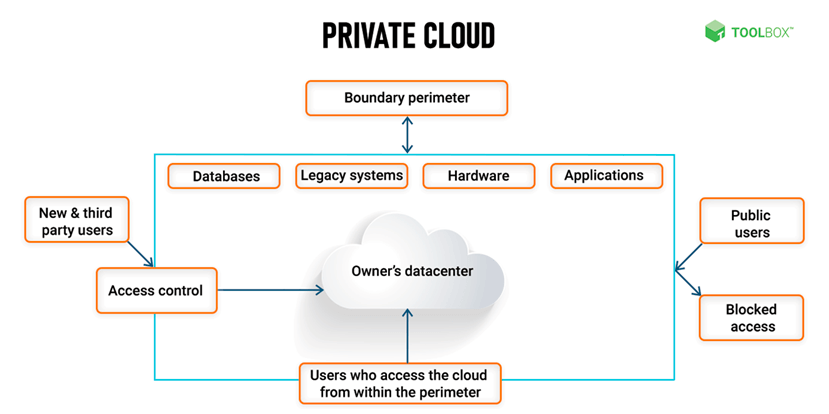

Unlike a public cloud, a private cloud is not shared with other organizations and is typically hosted on-premises or in a third-party data center. In a private cloud, the organization has full control over the computing resources, including the physical servers, storage, and network devices. This allows the organization to customize the infrastructure to meet business and security requirements.
For example, Microsoft Azure Stack is a private cloud provider. According to Statista, “37% of technical professionals are using Microsoft Azure Stack’s private cloud services, making it the most used private cloud provider in 2022.”
Advantages of Private Cloud
Let’s explore the advantages of using a private cloud.
- Greater control: With a private cloud, an organization has full control over its computing resources, including physical servers, storage, and network devices. This allows the organization to customize the infrastructure to meet its business and security requirements.
- Security and privacy: Since a private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, it offers greater security and privacy than a public cloud. Organizations can implement security policies and procedures and have greater visibility and control over their data.
- Performance and scalability: Private clouds can provide better performance and scalability than public clouds since they are not shared with other organizations. This allows organizations to scale resources to meet demand and ensure consistent performance.
- Customization: Private clouds can be customized to meet specific business requirements, allowing organizations to deploy applications and services tailored to their needs. This helps improve operational efficiency and enables organizations to gain a competitive edge.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
Let’s explore the disadvantages of a private cloud.
- High costs: Private cloud computing can be more costly than public cloud computing when considering the total cost of ownership. This can be particularly true in short-term use cases.
- Limited mobile access: Due to the multiple layers of security implemented in private cloud environments, mobile users may experience limited access to the resources available in the private cloud.
- Unable to keep up with unpredictable computing demands: Private cloud infrastructure may struggle to cope with unpredictable demand if the cloud data center is limited to on-premise computing resources.
Private vs. Public Clouds: Use Cases
Here, we will discuss the use cases for private vs. public clouds. The cloud is best suited for
| Private Cloud | Public Cloud |
| Industries and government agencies that are highly regulated. | Organizations with predictable computing needs. |
| Organizations that can afford to invest in high-performance and high-availability technologies. | Additional resources to address varying peak demands. |
| Companies that handle sensitive data. | Running essential apps and services required to perform IT and business operations. |
| Organizations that require high control and security over their IT workloads and infrastructure. | Software development and test environments. |
Difference Between Private and Public Clouds
This section will explore the key differences between private and public clouds.
- Infrastructure
A multi-tenant architecture characterizes public clouds, where multiple users share a network. The infrastructure is managed off-site by a service provider. On the other hand, a private cloud is a dedicated system for a single tenant that utilizes dedicated hardware. The infrastructure, including hardware, storage, and networking facilities, is procured and operated either on-site or off-site by an organization’s internal technical team without the involvement of a third-party vendor.
- Scalability and Reliability
Public clouds are highly scalable, allowing organizations to access virtually limitless resources for their cloud operations. Furthermore, public cloud providers offer built-in infrastructure security modules that enhance reliability.
On the other hand, private clouds offer limited scalability and may require additional hardware beyond a certain threshold. Nonetheless, private clouds are known for their reliability and can be configured to address contingencies.
- Security
Public clouds offer a security compliance model provided by third-party service providers and additional protection options offered by vendors to address any security gaps.
On the other hand, a private cloud offers a dedicated infrastructure with isolated servers that provide customizable levels of security. This makes it suitable for use cases with specific data protection requirements and regulations where enhanced security is necessary.
- Deployment & Maintenance
Public clouds allow fast and flexible deployment without long-term commitments. With hardware and network management handled by third-party vendors, organizations can minimize the time and resources needed for IT maintenance.
On the other hand, private clouds entail a substantial investment of time and effort from IT professionals for successful deployment, including software and hardware configuration and staffing. Tenants are responsible for setting up and maintaining the infrastructure, necessitating ongoing monitoring and supervision by qualified IT personnel.
- Control & Customization
Public clouds have data governance and privacy policy limitations, as third-party service providers govern them. Moreover, public clouds offer limited customization options.
Private clouds offer greater control over data governance and privacy policies since they are dedicated to a single tenant. Furthermore, private clouds are fully customizable and can be customized to meet specific requirements.
Hybrid Cloud: Bringing the Best of Private & Public Clouds Together
A hybrid cloud refers to a computing environment that combines various computing, storage, and services from multiple sources, including public clouds, private clouds, and on-premises data centers or “edge” locations, to run applications.
By adopting a hybrid cloud architecture, companies can reap the benefits of the public cloud’s scalability and low costs, as well as the private cloud’s privacy and control. Taikun offers businesses the flexibility of a hybrid cloud architecture to meet their needs and goals.
Taikun provides a comprehensive cloud management platform to enable businesses to better utilize public cloud services while keeping their critical applications and data secure in a private cloud. This allows businesses to improve their responsiveness, reliability, and productivity while meeting government regulations and maximizing output


