Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses used to run in the past. Currently, there are many models of cloud computing. Cloud technologies have matured, expanded, and improved to support business purposes.
According to Statista, “the global cloud applications market is expected to reach $168.6 billion by 2025.”
As a result of the proliferation of cloud technologies, businesses, particularly those new to the cloud, sometimes need clarification on multi-cloud and hybrid clouds. While they both refer to types of cloud deployment integrating multiple clouds, there are significant differences between them.
The article explores the key similarities and differences between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments.
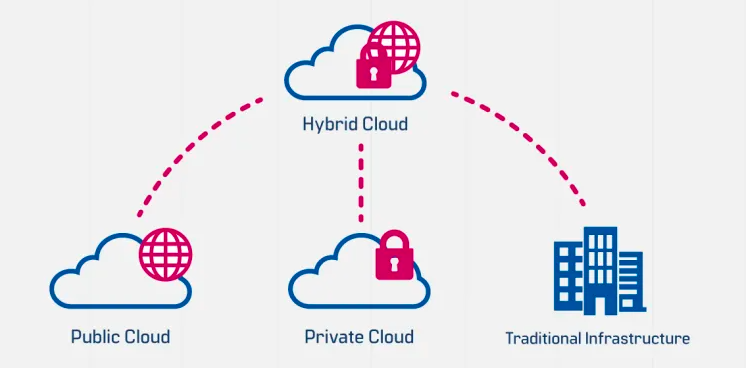
What is a Hybrid Cloud?
A hybrid cloud is a type of cloud deployment that integrates private and public cloud services and on-premise infrastructure while providing management, orchestration, and application portability across all three. This results in a unified and flexible distributed computing model where organizations can run and scale their legacy or cloud-native workloads. (Also, learn how to run applications on top of Kubernetes.)
In March 2022, 80% of the enterprise respondents indicated they had deployed a hybrid cloud in their organization. ~ Statista
A hybrid cloud approach enables organizations to benefit from the cost-efficiency and scalability of the public cloud while keeping sensitive information secure on a private cloud or on-premise.
What is Multi-Cloud?
A multi-cloud environment combines cloud services from more than one cloud vendor rather than combining public and private cloud services.
In 2021, 90% of respondents from large enterprises indicated having adopted multi-cloud, while smaller businesses lagged in terms of adoption. ~ Statista
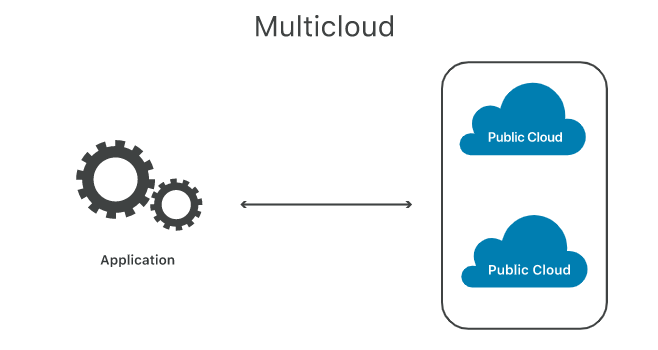

A multi-cloud solution is portable across multiple cloud providers’ infrastructures and is built on open-source, cloud-native technologies, such as Kubernetes, supported by all public cloud providers. This approach enables organizations to take advantage of different cloud providers’ unique features and capabilities and avoid vendor lock-in. Also, it allows you to speed up your workloads across multiple clouds for improved performance and security.
Comparing Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud: Similarities & Differences
Since multi-cloud and hybrid cloud deployments differ in purpose and architecture design, they have significant similarities and differences.
When asked about the primary uses of hybrid or multi-cloud deployments, the most frequent response by the respondents’ organizations was to accelerate development. ~ Statista
Talking about similarities, both multi-clouds and hybrid clouds have the following things in common:
- Store sensitive data: Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments use different cloud types, like private, on-premises, or public cloud. In both cases, storing sensitive data depends on the design and needs of the business. This means, in multi-cloud and hybrid environments, you can store critical data on-premise, on a private or public cloud, or an in-house server.
- Architecture security: Security in multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments highly depends on the system’s architecture. All vendor’s security protocols must be considered when using various public clouds to ensure a secure infrastructure. It’s important to work with trustworthy vendors and control security parameters to enhance security regardless of the deployed architecture.
- Manage regulation-specific data: When a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud setup does not include a private cloud, a company needs to ensure that the public cloud storage complies with regulations and protocols such as HIPAA or GDPR. This allows multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments to store regulation-specific data in a more secure, controlled, and isolated environment.
- Complex cloud migration: Moving data or applications to the cloud is a complex task that requires a significant amount of resources. Since in both environments, data has to be migrated to multiple clouds, which can be time-consuming and difficult. Therefore, cloud migration can be quite challenging in both multi-cloud and hybrid cloud setups.
Multi-cloud and Hybrid cloud setups:
- Provide flexibility and redundancy by allowing businesses to spread their workloads across multiple clouds, which can improve performance, security, and disaster recovery.
- Enable businesses to deploy highly suited infrastructures optimized for their specific needs and support capital investments’ transition into operational expenses by allowing businesses to pay for only the resources they use.
Differences Between Multi-Cloud & Hybrid Cloud
In this section, we will explore the differences between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud based on different characteristics, including architecture, intercloud workloads, vendor lock-in, availability, and cost.
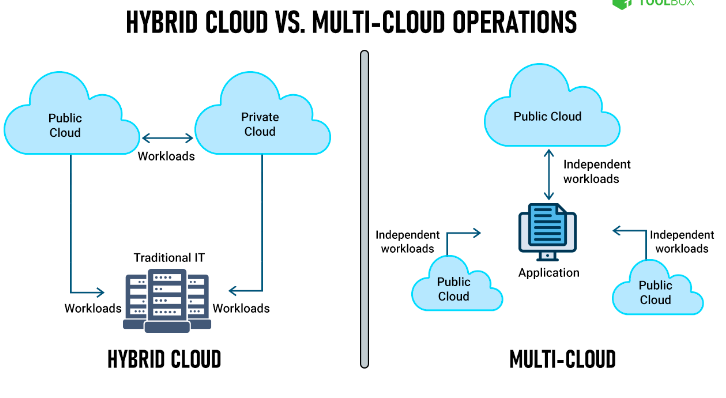

- Architecture
The multi-cloud architecture uses two or more clouds of the same type, while there is no communication between the clouds. Also, there is no central management for identity, logging, monitoring, alerting, or networking in a multi-cloud, making it harder to manage. You can store all kinds of data in multiple public clouds in a multi-cloud environment.
On the other hand, hybrid cloud architecture combines at least one private cloud or on-premise data center and one public cloud. The infrastructure components in a hybrid cloud setup share central management for identity, logging, monitoring and alerting, and networking. This makes it easier to manage and integrate the different components.
- Intercloud Workloads
Different clouds in a multi-cloud environment manage separate tasks and operate independently to manage data and associated processes. The different components work together in a hybrid cloud setting to run a single IT solution. As a result, data and processes interact with each other seamlessly.
- Vendor Lock-ins
Since a multi-cloud environment enables vendor-independent existence for organizations, it avoids vendor lock-ins, enabling the business to respond and adapt to evolving market demands. However, moving to a new vendor in a hybrid cloud setup becomes difficult, as the underlying cloud environment is customized to work in sync. Also, you may face downtime if any vendor transition takes place.
- Availability
High availability is an important benefit of a multi-cloud environment. It provides enterprises with a reliable cloud backup system with a standby option. This means that if one vendor experiences a temporary issue, the workload can be transferred to another vendor’s cloud, resulting in no downtime for end users.
On the other hand, maintaining availability depends upon the in-house teams in a hybrid cloud environment, as most of the workload is on-premise or on a private cloud.
- Cost
A company using multi-cloud services does not need to pay for on-premise infrastructure, but the relevant teams need to monitor and manage cloud expenses to prevent unnecessary spending.
A hybrid infrastructure utilizing a private cloud can effectively control costs as it only utilizes a single public cloud. However, organizations considering implementing this type of system should invest in hiring qualified personnel to manage the combination of private and public clouds efficiently.
Choosing the Best Cloud Environment for Your Business
The decision between a hybrid cloud or multi-cloud strategy is often determined by factors such as control and ownership. Determining the best approach is not always straightforward, but it should always align with the business’s specific needs and objectives.
When to choose a hybrid cloud: A hybrid cloud is suitable for organizations that require the benefits of cloud resources and services but have a legal or regulatory obligation to keep certain data or workloads in-house. For example, if a company wants to develop cloud-native applications but must run particular workloads on-premises.
When to choose a multi-cloud: A multi-cloud strategy is ideal for businesses that require specific services or resources from different cloud providers. For example, a company may choose to use virtual machines and storage from one provider, AI/ML services from another provider, and business applications from multiple SaaS providers.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to cloud architecture. Each option presents its own set of complexities and challenges; it’s important to understand them and choose the strategy that best fits the business’s needs and goals.
Supporting Your High-Performance Cloud Solution with Taikun
Effective cloud management is essential for businesses for optimized performance. However, managing a cloud environment can be complex and time-consuming. A cloud management platform, Taikun, can help you in this regard.
It provides companies with powerful features for managing their cloud infrastructure. With Taikun, you can easily manage your multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environment, freeing up time and resources to focus on core business processes.


